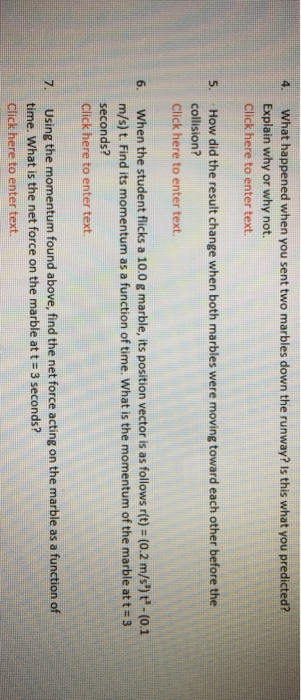
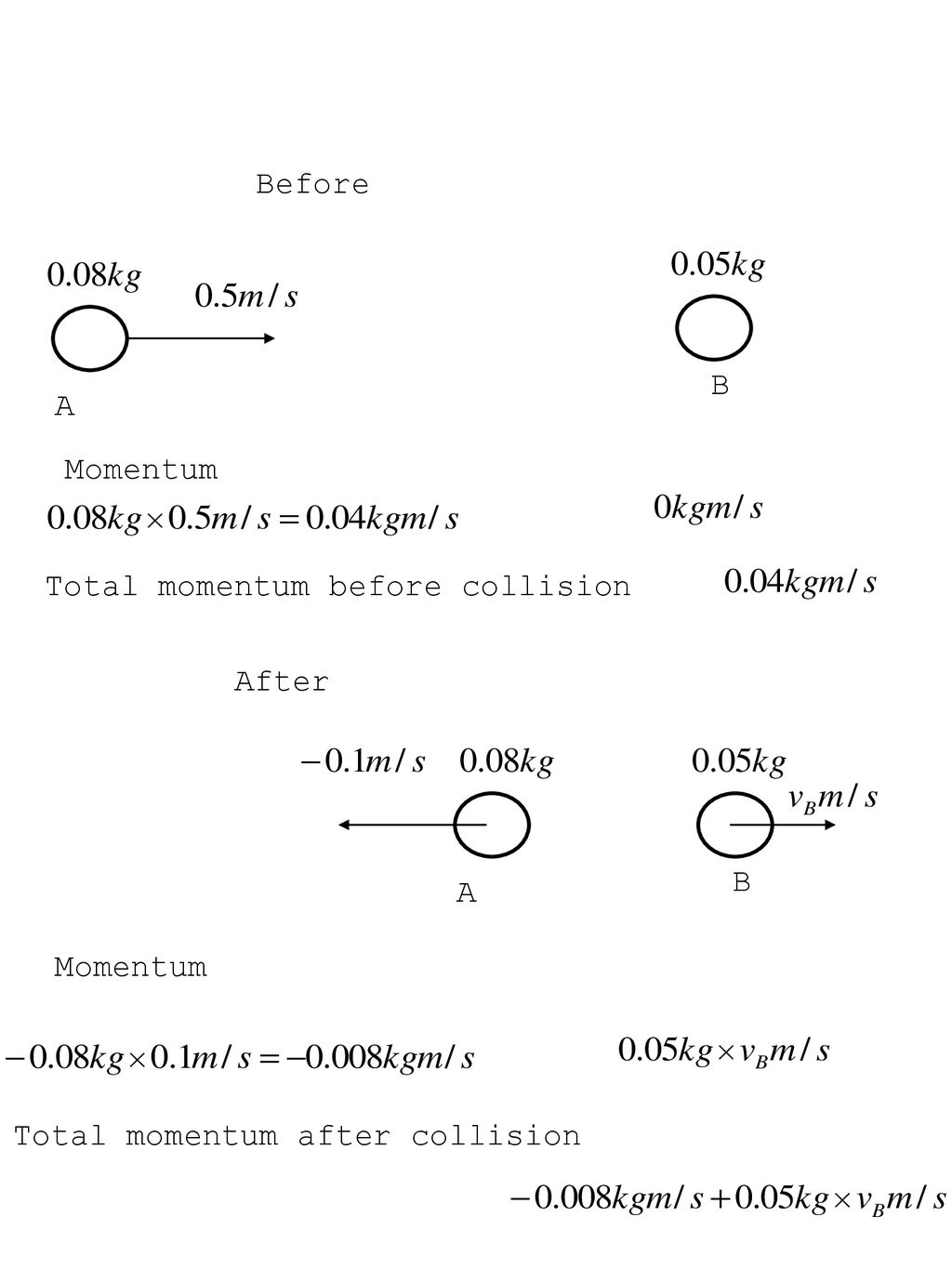
Marble Collision To Have Different Momentum What Is The Forces

In physics a collision doesn t have to involve an accident like two cars crashing into each other but can be any event where two or more moving objects exert forces on each other for a short period of time.
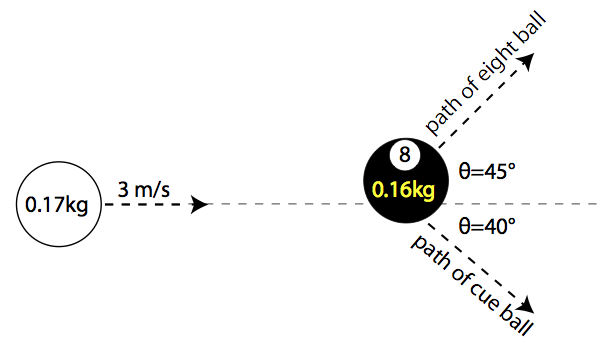
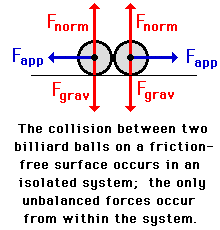
Marble collision to have different momentum what is the forces. An example of real objects that have approximately elastic collisions are billiard balls. Momentum is conserved in all collisions when no external forces are acting. Almost all collisions we encounter in this course are isolated. The top marble will have a greater initial momentum.
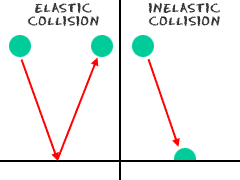
Two types of collisions are of interest. The perfectly inelastic collision momentum formula is the inelastic collision energy formula is elastic collisions in an elastic collision both momentum and energy are conserved. What would happen if you could throw a wrecking ball at the wall at the same speed that you threw the tennis ball. The smaller marble didn t have any original momentum.
So we can almost always assume that the total linear momentum is conserved. Conservation of momentum of systems when two objects a and b collide the collision can be either 1 elastic or 2 inelastic. The collision is almost instantaneous. In a collision of two cars of unequal mass the occupants of the lighter car would experience much higher accelerations hence much higher forces than the occupants of the heavier car.
If you throw a tennis ball at a wall it will bounce back toward you. Materials 2 balls of different masses objects in motion have momentum. Why would a wrecking ball have a different effect. In this case the forces between the colliding objects are conservative.
Momentum is a product of mass and velocity so if both marbles have equal masses whichever has a greater velocity will have a greater momentum. But what is the force that the first marble applied one the second marble. Collisions 2 conservation of linear momentum in collisions involved in isolated systems recall that linear momentum is conserved in isolated systems. However kinetic energy is conserved in elastic collisions only.
Collisions when two objects bump into each other this is called a collision. Because of the law of conservation of momentum the second marble now had the velocity of the first marble. Conserving momentum and energy it s the law. In both types of collision total momentum is always conserved.
Motion related energy is called kinetic energy energy due to an object s position or. We have been applying conservation of momentum to collisions and explosion which is valid but there are actually two different types of collisions and they have different properties. The wall would most likely break apart.